Most of the logic/code that used to be server-sided, is now moving to the client. It’s the framework that helps us to be more productive, removing the need to “reinvent the wheel” in every project.
In this article, we’re gonna discuss the top Front end Frameworks of the market and check the Pros and Cons of each one. Just to be clear, this won’t be a comparison between them; It’s a list with some frameworks that you should look at before starting a new project.
Since Javascript is the base of these frameworks and you prefer Front End projects but don’t have experience with Javascript, you may want to check out this project to learn how to create a web page from scratch.
With so many options, it may be difficult to choose a Javascript Framework, even though our only candidates ( most of the time) are Angular, React, and Vue.js. For beginners, it’s even harder to choose.
To simplify this quest, here goes the Best Front end Frameworks of 2020.
Our list, not by coincidence, is made of the 5 most well-known Front End Frameworks at the moment. If you’re a front end developer or intend to, these are your best bets:
There are many reasons for these frameworks to be included here, but the ones I’ll focus on are Popularity, Community, Performance, and Documentation.
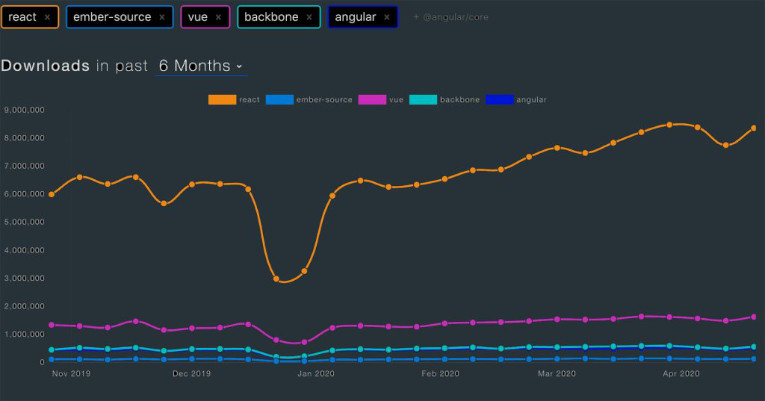
Here’s a graphic based on npm trends of the top 5 front end frameworks in the last six months. (npm is the package manager of Javascript).
As you can see, React dominates the download list by far, followed by (not even close) Vue.js
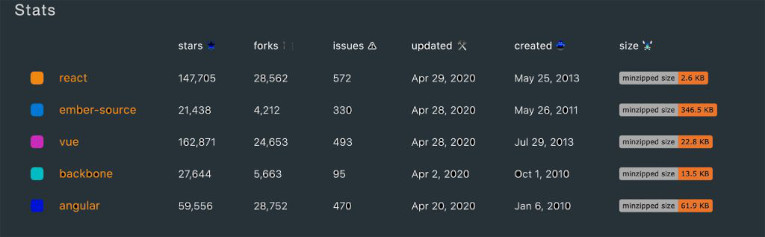
But React doesn’t dominate every single category of the frameworks front end. For example React loses to Vue.js in star count on Github, and by the number of forks for Angular. Each one has its spotlight.
React is the current leader of the JS world. This JS framework uses a reactive approach and introduces many of its concepts to the Front end development.
To use React, maybe you’ll need to learn some additional tools like Redux, MobX, Fluxy, Fluxible, RefluxJS, React-router, and so on.
A code example in React:
ReactDOM.render(
<h1>Debug Everything, world!</h1>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
Vue.js was a javascript framework designed from the start to be adopted gradually. The main library is focused only on the visualization layer. Vue.js is easy to integrate with other existing libraries or projects.
And you are perfectly capable of creating single-page applications (SPA) with Vue.js when used in combination with other tools and support libraries.
One of Vue.js biggest advantages is its size. We’re talking about an 18-21KB framework.
A code example in Vue.js:
<!--Html-->
<div id="app">
{{ message }}
</div>
//Javascript
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
message: 'Debug Everything!'
}
})
You can’t have a list of the best front end frameworks without mentioning Angular. Angular is the only javascript framework that is based on TypeScript in this list.
Unlike React, and like Vue.js, Angular also uses the two-way data binding model. It means that there is a real-time synchronization between Model and View, where any change in Model instantly reflects on the Views and vice versa.
If your project involves building mobile or web applications, this javascript framework is a good alternative.
Compared to React and Vue.js. Angular is not easy to learn. Although there are numerous documentation available, they are very complex or confusing.
A code example in Angular:
//javascript
@Component({
selector: 'main-app',
template: ` <p>
Debug Everything
</p>`,
})
export class MainAppComponent {
constructor() { }
}
Ember is one of the oldest javascript frameworks, coming before Angular JS, for example.
Ember has a relatively complicated architecture. It is one more in the list of javascript frameworks that use the MVC structure.
One of Ember’s best features is its command-line interface (CLI). Not only can you create new projects with ready-made configurations, but you can also create controllers, components, and project files using automatic generation.
A code example in Ember.js:
//Javascript
export default Ember.Component.extend({
componentGreeting: 'Debug Everything'
})
<!-- HTML -->
<h2 class="title">{{componentGreeting}}</h2>
The latest javascript framework on our list is not a javascript framework, just like React, Backbone.js is a library.
When working on a web application that involves a lot of JavaScript, one of the first things you learn is to stop tying your data to the DOM.
With Backbone, you can represent your data as models, which can be created, validated, destructed, and saved in the server.
Backbone.js is a really light library judging by the features and structures it delivers. It is essentially MVC for the client, allowing you to create your code in a modular way.
Also, it reinforces that the communication between client and server must be entirely made by a Restful API.
Backbone.View, you need jQuery.A code example in Backbone.js
// Javascript
var AppView = Backbone.View.extend({
el: '#container',
initialize: function(){
this.render();
},
render: function(){
this.$el.html("Debug Everytthing");
}
});
As you may have noticed, every JS framework suffers from one problem or another. None of them is the “perfect solution” if it really exists.
The most important thing is for you to evaluate your project, plan it today, and in 5 years. Scalability and maintainability are major points for a project lifespan.
And also, the JS framework choice doesn’t need to be final; You can always make a transition if necessary. Or even fuse frameworks together, like the Angular JS framework and the React library for example. It isn’t ideal, but hey, nothing stops you.
Microsoft is already doing that!
Well, I hope you liked the reading. If you did, subscribe to receive news and great exclusive content!
Until next time.
Leave a Reply